Endoscopic Surgeon Action Detection
A novel approach using STN and EfficientNet-B2 with FPN for minimally invasive surgery.
View Challenge
Kidney Tumor Detection
Advanced imaging and ML for accurate kidney tumor detection and classification.
PDF Chatbot
Intelligent system for enhanced interaction with PDF documents using BERT and PSO.
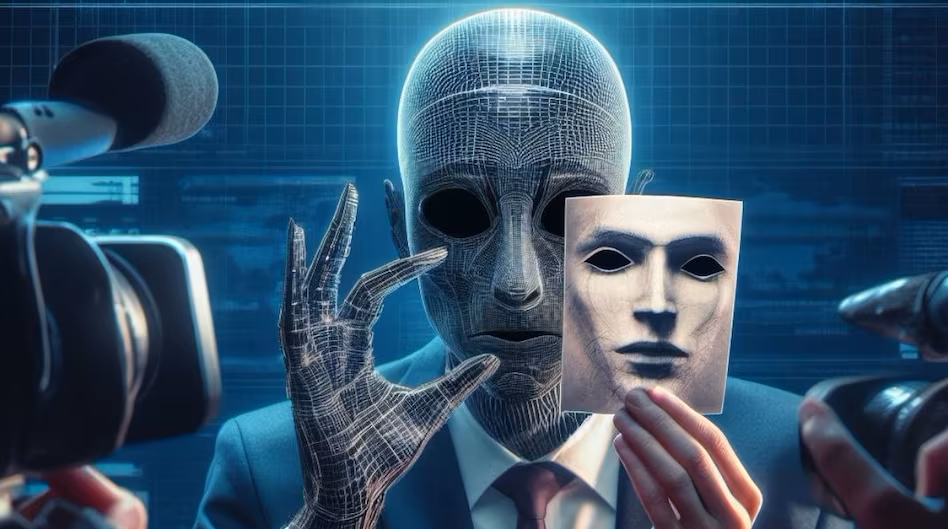

Deep Fake Image Detection using Deep Learning Models
The "Deep Fake Image Detection using Deep Learning Models" project uses InceptionResNetV2 and EfficientNet to detect digitally manipulated images. These models identify subtle artifacts that reveal image manipulation, providing an effective tool for ensuring digital media integrity and combating misinformation.
Emotion Detection through Facial Expression and Voice
The "Emotion Detection through Facial Expression and Voice" project combines advanced deep learning techniques to accurately identify human emotions by analyzing both facial expressions and vocal tones. The system uses specialized deep learning models for facial expression recognition and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for voice emotion analysis. When a user appears in front of a camera, the system captures a video frame to detect facial expressions and simultaneously processes the audio to identify emotions in the voice. This dual approach ensures comprehensive and precise emotion detection from a single input source, whether it's a live webcam feed, live video, or recorded video file. By integrating these technologies, the project delivers a reliable tool for real-time and recorded emotion analysis, applicable in various fields such as mental health, customer service, and human-computer interaction.
Detection of Human vs. Bot-Generated Text on Twitter Using Deep Learning
The "Detection of Human vs. Bot-Generated Text on Twitter Using Deep Learning" project focuses on distinguishing between human-written and bot-generated tweets. Leveraging a hybrid model combining BERT, CNN, and LSTM architectures, the system analyzes text features to accurately classify the origin of Twitter content. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) provides contextual understanding of the text, while CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks) captures local patterns, and LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) networks model the sequential dependencies within the text. This integrated approach enhances the detection accuracy, making the system a robust tool for identifying automated content on social media platforms, thereby contributing to the integrity of online communication.
Image Captioning
The "Image Captioning" project aims to generate accurate and meaningful textual descriptions of images by integrating advanced deep learning techniques. This system employs EfficientNet for image classification to extract detailed features from images and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) for generating coherent and contextually relevant captions. EfficientNet's robust image classification capabilities ensure precise feature extraction, while BERT's powerful language modeling capabilities enable the creation of high-quality textual descriptions. By combining these models, the project achieves a sophisticated and effective image captioning system that can be applied to various domains, including digital media, accessibility, and automated content generation.
Plant Leaf Disease Detection and Care
The "Plant Leaf Disease Detection and Care" project aims to identify and manage plant diseases through advanced image recognition techniques. Utilizing MobileNet for its efficient and accurate image classification, the system can detect various plant leaf diseases from images. MobileNet's lightweight architecture ensures rapid processing and high accuracy, making it ideal for mobile and edge device applications. Once a disease is identified, the system provides detailed care instructions to help mitigate and treat the detected condition. This integration of disease detection and care guidance offers a comprehensive solution for farmers, gardeners, and agricultural professionals, promoting healthier plants and more effective disease management practices.
Skin Lesion Recognition through Federated Learning Approach
The "Skin Lesion Recognition through Federated Learning Approach" project aims to accurately detect skin lesions while maintaining data privacy and security. By employing federated learning, the project leverages data from multiple decentralized clients without transferring sensitive medical information to a central server. This distributed approach allows the global model to benefit from a diverse dataset, enhancing its accuracy and generalizability. The project uses EfficientNet, a state-of-the-art deep learning model, to improve the precision of skin lesion detection. EfficientNet's robust feature extraction capabilities, combined with federated learning's privacy-preserving method, create a powerful tool for dermatological diagnostics, offering improved detection and classification of skin lesions while safeguarding patient privacy.
Restaurant Reviews Prediction
The "Restaurant Reviews Prediction" project aims to automatically predict star ratings for restaurant reviews using advanced natural language processing techniques. Leveraging BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), the project trains a model on a dataset of restaurant reviews and their corresponding ratings, ranging from 1 to 5 stars. BERT's powerful contextual understanding of language allows the model to accurately capture the nuances and sentiments expressed in the reviews. As a result, the system can predict the appropriate star rating for new reviews based on their textual content. This automated prediction tool can assist restaurant owners in understanding customer feedback, enhancing service quality, and providing insights for potential improvements.
Knee Osteoarthritis Detection
The "Knee Osteoarthritis Detection" project focuses on the early and accurate detection of knee osteoarthritis (OA) using advanced deep learning techniques. Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Early detection is crucial for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. The project utilizes MobileNet, a lightweight yet powerful deep learning model, to analyze medical images of knees for signs of osteoarthritis. MobileNet's efficient architecture allows for high accuracy and rapid processing, making it suitable for deployment on various devices, including mobile and edge computing platforms. By training the model on a comprehensive dataset of knee images, the system can effectively identify the presence and severity of osteoarthritis, providing valuable diagnostic support to healthcare professionals and aiding in timely intervention and treatment planning.
Early Detection of Alzheimer's Disease Using Transformer Models
The "Early Detection of Alzheimer's Disease Using Transformer Models" project aims to improve the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease through advanced deep learning techniques. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that leads to cognitive decline and memory loss. Early detection is vital for effective intervention and management. This project employs the Swin Transformer, a state-of-the-art deep learning model known for its superior performance in image classification tasks, to analyze brain imaging data for early signs of Alzheimer's. The Swin Transformer's hierarchical vision transformer architecture allows it to capture intricate details and patterns within the images, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. By training the model on a robust dataset of brain images, the system can identify subtle biomarkers indicative of Alzheimer’s, facilitating early diagnosis and timely treatment, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and advancing neurological research.
GuardianAI: Predictive Models for Cyber Bullying Detection
"GuardianAI: Predictive Models for Cyber Bullying Detection" addresses the growing concern of online harassment by developing machine learning models to automatically identify cyber bullying in text data. Cyber bullying, a pervasive issue in digital communication, can have severe psychological impacts on victims. This project employs Random Forest, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Decision Tree algorithms to analyze text and predict instances of cyber bullying. By training these models on labeled datasets containing examples of cyber bullying and benign text, the system learns to recognize patterns indicative of harmful behavior. Through rigorous evaluation and comparison, this study aims to determine the most effective model for cyber bullying detection, empowering platforms and users to take proactive measures to combat online harassment and foster a safer online community.
Visionary Dermatology: Advancing Skin Lesion Classification with Vision Transformer Models
"Visionary Dermatology: Advancing Skin Lesion Classification with Vision Transformer Models" revolutionizes dermatological diagnostics by harnessing the power of Vision Transformer models. Skin lesions present a diverse array of conditions, from harmless moles to potentially life-threatening malignancies, demanding precise and timely identification. This project leverages Vision Transformer models, renowned for their prowess in image classification tasks, to analyze dermatological images and accurately classify skin lesions. Trained on a rich dataset encompassing various lesion types, the system learns intricate patterns and features critical for nuanced diagnosis. Through rigorous evaluation, this study showcases the transformative potential of Vision Transformer models in elevating dermatological diagnostics, promising improved patient care and fostering advancements in dermatology research.
"EfficientNet-ViT Fusion for Leukemia Detection: Advancements in Medical Imaging Analysis"
This project employs a fusion of EfficientNet and Vision Transformer (ViT) models to enhance the detection and classification of leukemia from medical imaging data. Leukemia, a complex blood cancer, demands early and accurate diagnosis for effective treatment planning. The EfficientNet-ViT fusion leverages EfficientNet's efficient feature extraction capabilities alongside Vision Transformer's attention mechanism for comprehensive image analysis. By training on annotated datasets of peripheral blood smear images and bone marrow biopsy slides, the system learns to distinguish between healthy and leukemic cells with high accuracy. This innovative approach holds significant promise for improving leukemia detection rates and facilitating timely interventions in clinical settings.
ResNet: Empowering Brain Tumor Detection through Deep Learning
This study delves into the realm of brain tumor detection using ResNet, a deep learning architecture renowned for its effectiveness in image classification tasks. Brain tumors present a significant medical challenge, necessitating timely and accurate diagnosis for appropriate treatment planning. Leveraging ResNet's robust feature extraction capabilities, this project aims to analyze magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and identify regions indicative of brain tumors. By training the ResNet model on large datasets comprising diverse brain tumor cases, the system learns to discern between healthy brain tissue and tumor-afflicted regions with high precision. This research holds promise for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and expediting treatment initiation for patients with brain tumors.
Deep Learning for Chest X-ray Analysis: Unveiling Insights with Convolutional Neural Networks
This study explores the utility of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in the analysis of chest X-ray images for medical diagnosis. Chest X-rays serve as a crucial diagnostic tool for detecting various pulmonary conditions, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. Leveraging the capabilities of CNNs, this research aims to automatically extract informative features from chest X-ray images and identify abnormalities indicative of underlying respiratory ailments. By training the CNN model on extensive datasets comprising diverse chest X-ray images, the system learns to accurately differentiate between healthy and diseased lung tissue. This investigation showcases the potential of deep learning techniques in revolutionizing chest X-ray analysis, offering clinicians valuable insights for timely and effective patient care.
TGRTC Bus Prediction: Assessing Student Arrival Time with Machine Learning Models
The "TGRTC Bus Prediction" project aims to predict whether students can reach their destination on time by utilizing RTC bus services. The project gathers data from RTC bus stops, including bus schedules, routes, and environmental factors such as weather conditions and traffic patterns. Leveraging machine learning models including Support Vector Machines (SVM), Decision Trees, and Naive Bayes classifiers, the system analyzes the collected data to forecast the likelihood of students arriving on time based on various criteria. By integrating real-time information and historical data, the project provides valuable insights for students planning their commute, helping them make informed decisions to optimize their travel time and ensure punctual arrival at their destination.